|
Calandrella cinerea (Red-capped lark)
Rooikoplewerik
[Afrikaans]; Intibane, Intutyane [Xhosa]; umNtoli [Zulu]; Thesta-balisana,
Tsiroane [South Sotho]; Roodkapleeuwerik [Dutch]; Alouette cendrille
[French]; Rotscheitellerche [German]; Cotovia-de-barrete-vermelho
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Alaudidae
 |
 |
|
Red-capped lark adult, Intaka Island Wetland
Reserve, South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Red-capped lark juvenile, Tanqua Karoo, South
Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from southern DRC and Kenya through Zambia and
Angola to southern Africa. Here it is common to abundant in open grassland,
shrubland (such as Karoo and fynbos), and saltmarsh vegetation along lagoon
shores. It also favours recently ploughed, harvested or burnt fields and road
verges after rainfall.
|
 |
|
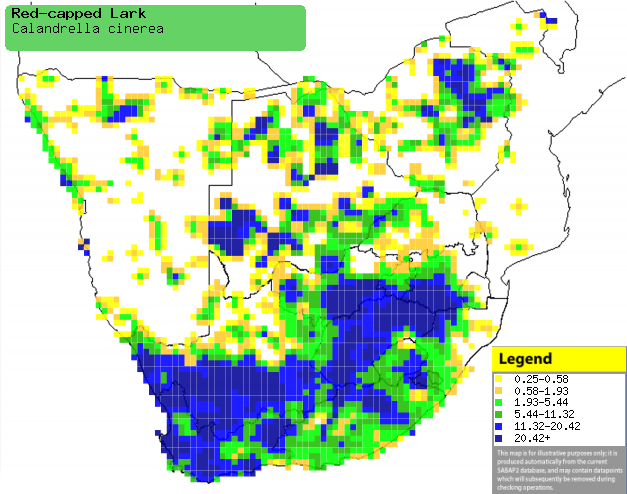
Distribution of Red-capped lark in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It mainly eats seeds supplemented with invertebrates,
plucking food items from bare soil and occasionally taking prey from grass tufts
and shrubs. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Seeds
- Grasses
- Brachyaria
- Setaria
- Urochloa
- Eleusine
- Panicum
- Sedges
- Shrubs
- Forbs
- Amaranthus
- Arctotis
- Dimorphotheca
- Gisekia
- Mollugo
- Aizoaceae
- Invertebrates
Breeding
- The nest (see image below) is built mainly by the female in about 4-5
days, consisting of a cup built of dry grass and roots and lined with finer
plant fibres. It is typically placed on the ground in a scrape, hole or deep
hoofprint, often located next to a grass tuft, clod of earth or animal dung.
 |
|
|
Red-capped lark nest with eggs, Wakkerstroom,
South Africa. [photo
Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- The eggs are usually laid just before rainfall in the period from
March-December, peaking from July-September
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
12-15 days, while the male feeds her at the nest.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 9-18
days.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact it has greatly benefited from the
introduction of farmland, which is know one its favourite habitats.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
