|
Calendulauda africanoides (Fawn-coloured lark)
[= Mirafra africanoides]
Vaalbruinlewerik [Afrikaans]; Yisimatuli (generic term for
lark) [Kwangali]; Mapuluhweni (generic term for lark) [Tsonga]; Sebotha
(generic term for lark) [Tswana]; Savanne-leeuwerik [Dutch]; Alouette
fauve [French]; Steppenlerche [German]; Cotovia-cor-d'areia [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Alaudidae
> Genus: Calendulauda
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to southern Africa, from north-central South
Africa to Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe and Mozambique, marginally extending into
Zambia and Angola. It generally prefers habitats with sandy soils, such as
fine-leaved and broad-leaved savanna, dune shrubland, and in the Northern Cape
also occurring in grassland with scattered Greenhair-thorns (Parkinsonia
africana).
|
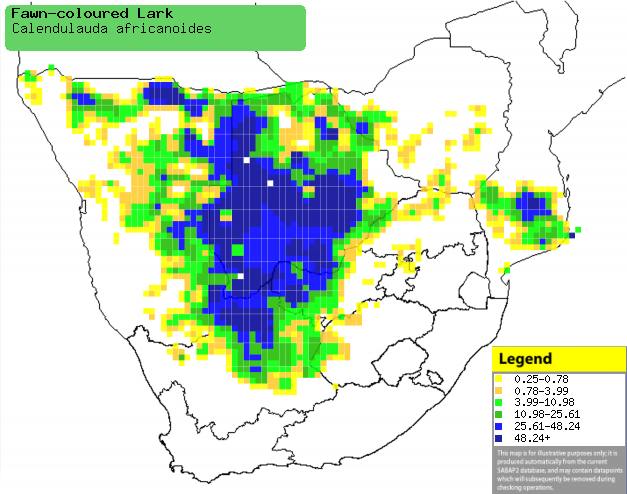 |
|
Distribution of Fawn-coloured lark in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of the following animals:
Food
It eats insects and the seeds of forbs and grasses, doing
most of its foraging on bare sandy soil and at the bases of grass tufts. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is cup built of grass and rootlets, often concealed by a
grass-built dome. It is typically placed in a scrape in the ground, at the
base of a small shrub or grass tuft.
- Egg-laying season is from September-April.
- It lays 2-3, rarely 4 eggs, which are incubated for about 12 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 12-14
days but becoming independent quite a long while after that
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
