|
Calendulauda burra (Red lark)
[= Mirafra burra]
Rooilewerik
[Afrikaans]; Alouette ferrugineuse [French]; Oranjelerche [German];
Cotovia-vermelha [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Alaudidae
> Genus: Calendulauda
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to the Northern Cape, South Africa, preferring red
sand dunes and sandy plains with grass with large seeds (such as Brachiara
glomerata, Stipagrostis ciliata and Stipagrostis brevifolia) and
scattered Greenhair-thorn trees (Parkinsonia africana). It may also occur
in dwarf shrubland with a substrate of shales, provided that there are enough
large-seeded grasses.
|
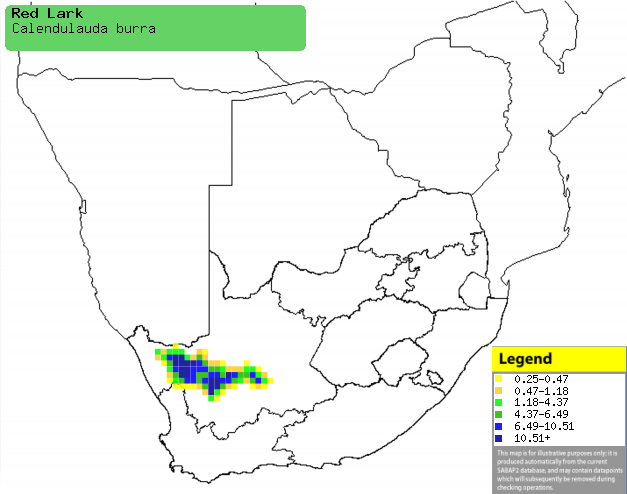 |
|
Distribution of Red lark in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It eats a variety of in insects and seeds, doing most of
its foraging on the ground, digging to expose food items with its large bill or
gleaning from the bases of plants. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Seeds
- grass
- Brachiara glomerata (signal grass)
- Stipagrostis ciliata (bushman grass)
- shrubs
- Giseckia pharnacioides (Volstruisduiwe)
- Tetragonia echinata (Kinkelbos)
- Limeum africanum (Koggelmandervoetkaroo)
- Limeum myosotis
- Tribulus terrestris (Dubbeltjie)
- Hermannia
- daisies
- Chenopodium (misbredjies)
- Lotononis
- Polygonum
- Fruit of honey-thorns (Lycium)
Breeding
- The nest is a domed cup built of thick-stemmed grasses, typically placed
in a scrape in the ground against one or two grass tufts. It is lined with
finer plant material, such as old weathered grass and the awns of bushman
grasses (Stipagrostis).
- It lays 2-3 eggs opportunistically after rain, usually in the months
from August-May, peaking in October.
- The chicks are fed by both parents on a diet of invertebrates, such as
bagworm caterpillars (Psychidae)
Threats
Vulnerable due to its localised and patchy
distribution along with destruction and fragmentation of its preferred habitat,
often due to livestock grazing. Its estimated population in 1991 was about 9400
birds and decreasing.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
