|
Calendulauda sabota (Sabota lark)
[= Mirafra sabota]
Sabotalewerik [Afrikaans]; Yisimatuli (generic term for lark) [Kwangali];
Urimakutata, Vhumakutata [Tsonga]; Sebotha (generic term for lark)
[Tswana]; Sabota-leeuwerik [Dutch]; Alouette sabota [French]; Sabotalerche
[German]; Cotovia-sabota [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Alaudidae
> Genus: Calendulauda
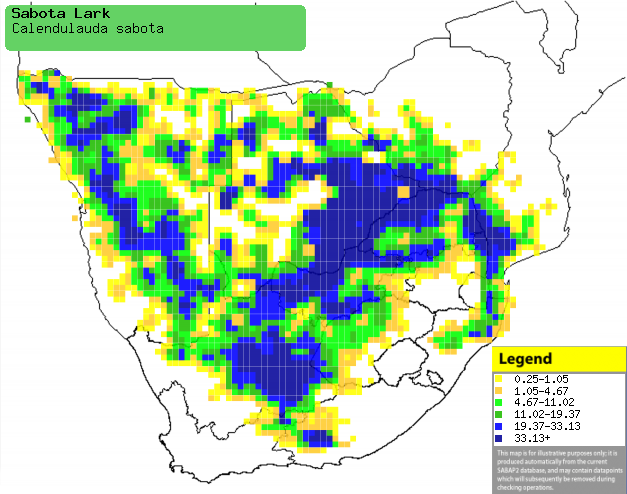
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to southern Africa, occurring across much of
the region and extending into western Angola. It is quite common in savanna and
open woodland, especially in areas with clay and rocks with Acacia and
Mopane (Colosphermum mopane), but also in woodland along drainage
lines in the Karoo.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Sabota lark in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of the following animals:
- Felis nigripes (Black-footed cat)
- Tyto alba
(Barn owl)
Food
It eats a variety of insects and seeds, doing most of its
foraging on open ground, gleaning food from the soil and bases of grass tufts
and shrubs. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Insects
- Seeds
- grasses
- Brachiara glomerata (Signal grass)
- Heteropogon contortus (Tanglehead
- Schmidtia kalihariensis (Kalahari sandkweek)
- Stipagrostis (bushman grasses)
- Panicum (guinea grasses)
- Setaria (bristle grasses)
- forbs
- Amaranthus (pigweeds)
- Chenopodium (misbredies)
- Cleome (spiderflowers)
- Indigofera (indigos)
- Tetragonia echinata (Kinkelbos)
- Polygala leptophylla (Skaap-ertjie)
- Galenia
- Limeum
- Molugo
- Trianthema
- Tephrosia
Breeding
- The nest is a cup built of dry grass and lined with finer plant material,
typically placed in the shade of a tuft of grass, shrub or rock. It often
builds a dome over the nest to protect against sunlight, however this only
done when there isn't much shade.
- It lays 2-4 white speckled eggs, usually in the months from October-May.
- Little is known about the chicks, other than that they are fed by both
parents.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
