|
Mirafra rufocinnamomea (Flappet
lark)
Laeveldklappertjie [Afrikaans]; uQaqashe [Zulu]; Yisimatuli
(generic term for lark) [Kwangali]; Chitambirmbuya [Shona]; Mamhengele,
Matharhatharha, Phapharharha [Tsonga]; Sebotha (generic term for lark)
[Tswana]; Ratelleeuwerik [Dutch]; Alouette bourdonnante [French];
Baumklapperlerche, Zimtbaumlerche [German]; Cotovia-das-castanholas
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Alaudidae
> Genus: Mirafra
Distribution and habitat
Occurs much of sub-Saharan Africa (excluding lowland
forests), from Senegal to Ethiopia south to southern Africa. Here it is fairly
common in grassy clearings and drainage lines within broad-leaved woodland,
especially Burkea (Burkea africana), miombo (Brachystegia) and
Zambezi teak (Baikiaea plurijuga), also occupying coastal grassland and
Acacia savanna.
|
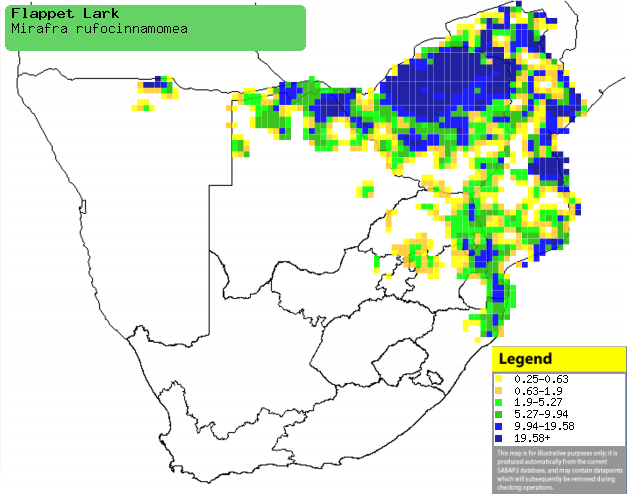 |
|
Distribution of Flappet lark in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It eats invertebrates and grass seeds, doing most of its
foraging on the ground. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Grass seeds
Breeding
- The nest is a partially or completely domed cup, built of dry grass and
lined with rootlets. It is typically placed in a scrape or hollow in the
ground adjacent to a tuft or two of grass, the leaves of which are
incorporated into the dome.
- Egg-laying season is from October-April, peaking from November-February.
- It lays 2-3 dull white eggs, which are speckled, spotted or streaked
with brown and grey.
- The chicks leave the nest after about 11 days, before they are able to
fly.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
