|
Chrysococcyx klaas (Klaas's cuckoo)
Meitjie [Afrikaans]; Klaaskoekoek [Dutch]; Coucou de Klaas [French];
Klaaskuckuck [German]; Cuco-bronzeado-menor [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Cuculiformes > Family: Cuculidae
The Klaas's cuckoo is fairly common across sub-Saharan
Africa, absent only from arid desert, usually occupying broad-leaved woodland.
It is mainly insectivorous, specializing in butterflies and caterpillars. It is
a brood parasite, meaning that it lays its eggs in other birds nests. The host,
thinking that the egg is its own, incubates the egg, and cares for the chick. It
lays 1 egg per nest, laying roughly 24 eggs in one breeding season. The
chicks usually hatch after an incubation period of about 11-12 days. Soon after
hatching, the chick evicts any of the host's chicks or eggs that are present in
the nest. It stays in the nest for about 19-21 days, after which it remains with
the host bird for up to 25 days.
Distribution and habitat
Fairly common across sub-Saharan Africa, absent only from
arid desert. In southern Africa it is fairly common in central and northern
Namibia, northern and eastern Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Swaziland and
southern and eastern South Africa. It generally
prefers open broad-leaved woodland, especially miombo (Brachystegia) and Mopane
(Colosphermum mopane) woodland, but
it also occupies dense Acacia thickets, forest edges, gardens and alien
tree stands around farmsteads.
|
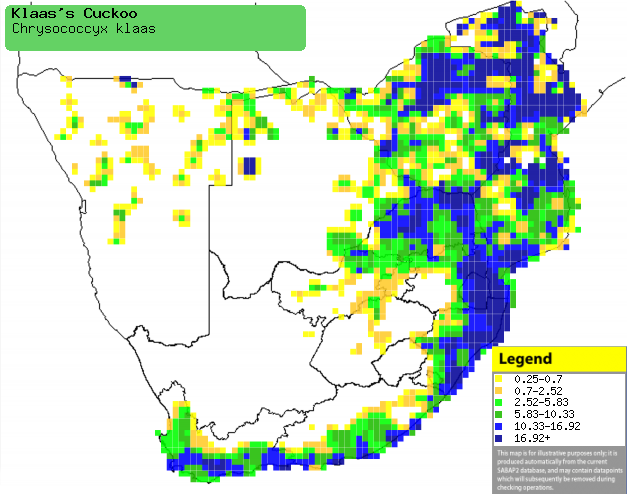 |
|
Distribution of Klaas's cuckoo in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
Mainly insectivorous, specializing in
butterflies and caterpillars. It usually forages in the foliage of trees or
bushes, taking insects from leaves and occasionally hawking a flying insect. The following food items have been
recorded in its diet:
Breeding
- It is a brood parasite, meaning that it lays its eggs
in other birds nests. The host, thinking that the egg is its own, incubates
the egg and cares for the chick. The following bird species have been parasitized by the Klaas's
cuckoo:
- Egg-laying
season is year-round, peaking from October-January.
- It lays one egg per nest, laying roughly 24 eggs in one breeding season. The chicks usually hatch after an incubation period of about 11-12 days.
- Soon after hatching, the chick evicts any of the host's chicks or eggs
that are present in the nest. It stays in the nest for about 19-21 days,
after which it remains with the host bird for up to 25 days (see image
below).
Threats
Not threatened, in fact its distribution range seems to
have expanded recently.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
