|
Amadina erythrocephala
(Red-headed finch)
Rooikopvink [Afrikaans]; Kafilita [Kwangali]; Jeremane
[South Sotho]; Roodkopamandine [Dutch]; Amadine à tête rouge [French];
Rotkopfamadine [German]; Degolado-de-cabeça-vermelha [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora >Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Estrildidae
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to southern Africa, occurring from
south-western Zimbabwe through Botswana and much of South Africa to Namibia and
south-western Angola. It generally prefers open desert grassland, arid savanna,
shrubland, croplands and farmyards.
|
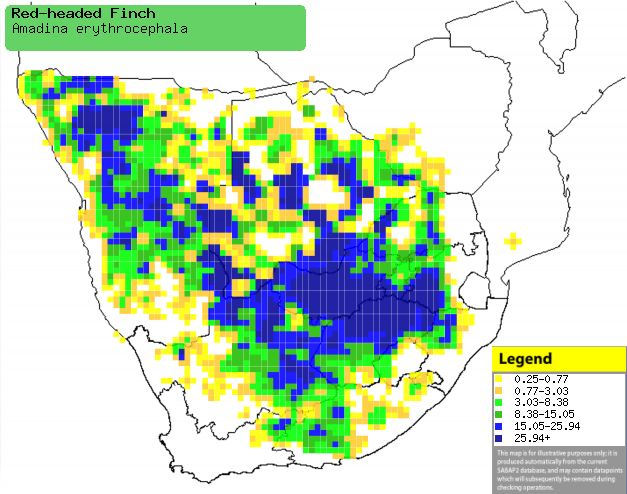 |
|
Distribution of Red-headed finch in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
It has been recorded as prey of
Falco chicquera
(Red-necked falcon).
Movements and migrations
Highly nomadic in the non-breeding season.
Food
It does most of its foraging on the ground, feeding on
small seeds and insects.
Breeding
- The nest can be either a small pad or a ball, made of grass and lined with
feathers. It is typically placed in an old nest of another bird, such as a
Ploceus weaver,
Red-billed buffalo weaver,
Cape sparrow or a
Sociable weaver, although
it may occasionally use a hole in a tree or building instead.
- It can breed at any time of year in response to rainfall, but egg-laying
season is usually from February-September.
- It lays 2-11, usually 4-6 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for
about 12-14 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after about 15-21
days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
