|
Indicator variegatus
(Scaly-throated honeyguide)
Gevlekte heuningwyser [Afrikaans]; Intakobusi (generic
term for honeyguide) [Xhosa]; iNhlava (also applied to Lesser honeyguide)
[Zulu]; Hlalala, Nhlampfu [Tsonga]; Schubkeel-honingspeurder [Dutch]; Indicateur
variť [French]; Gefleckter honiganzeiger [German]; Indicador-de-peito-escamoso
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Piciformes
> Family: Indicatoridae
 |
 |
|
Scaly-throated honeyguide, Arabuko-Sokoke forest,
Kenya. [photo Steve Garvie
©] |
Scaly-throated honeyguide, Kruger National Park,
South Africa. [photo Francois Dreyer
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across sub-Saharan Africa; in southern Africa it is fairly
common but localised in central and southern Mozambique, eastern Zimbabwe,
Swaziland and eastern and southern South Africa. It generally prefers coastal, montane and riparian forest, dense miombo (Brachystegia) woodland and valley bushveld; it is most common in mosaics of forest and woodland.
|
 |
|
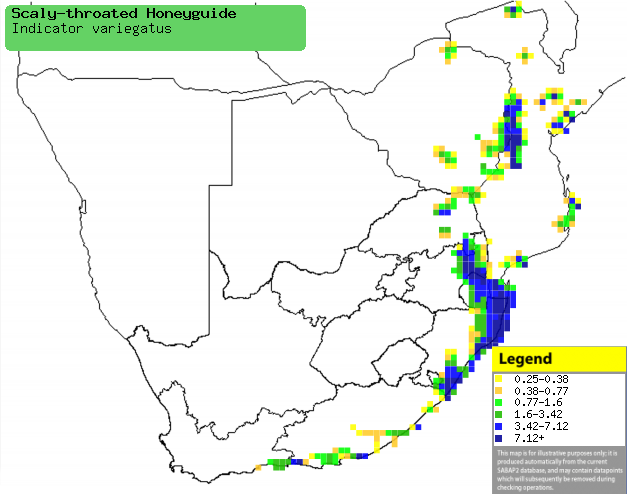
Distribution of Scaly-throated honeyguide in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements and migrations
Resident and sedentary.
Food
Mainly eats beeswax, honeybees (Apis mellifera)
and other insects, doing most of its foraging by hawking prey from a perch
or by seeking out beehives. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Beeswax
- Insects
- Seeds and fruit (rarely)
Breeding
- Territorial, polygynous and brood parasitic (laying its eggs in other
birds' nests), as each male copulates with multiple females within his
calling territory.
- The following birds have been recorded as host of the Scaly-throated
honeyguide:
- Egg-laying season is from September-January, peaking from
September-December.
- It lays a single egg per host nest, which is probably incubated for
about 18 days.
- The chicks are thought to kill the chicks of the host, leaving the nest
after about 27-35 days and soon becoming fully independent.
Threats
Not-threatened, although destruction and transformation of
woodland-forest mosaics is cause for concern.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
