|
Stactolaema whytii (Whyte's
barbet)
Geelbleshoutkapper [Afrikaans]; Whyte-baardvogel
[Dutch]; Barbican de Whyte [French]; Spiegelbartvogel [German]; Barbaças de
Whyte [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Piciformes >
Family: Lybiidae
 |
|
|
Whyte's barbet, Ewanrigg Botanical Gardens,
Zimbabwe. [photo
Ian Nason ©] |
|
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from southern Tanzania, through Zambia and Malawi, to
eastern Zimbabwe and central Mozambique. It generally prefers climax and well developed miombo (Brachystegia)
woodland on basal granite, especially if they are plenty of wild figs (Ficus).
|
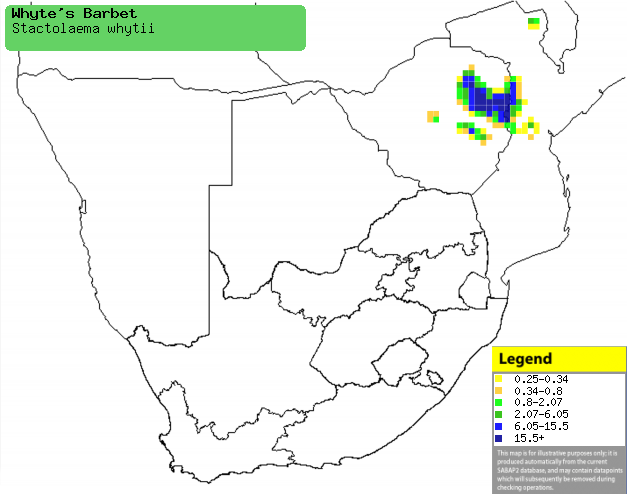 |
|
Distribution of Whyte's barbet in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Scaly-throated honeyguide.
Movements and migrations
Resident and locally nomadic, moving in
response to the availability of fruit.
Food
Mainly eats fruit taken directly from plants, supplemented
with nectar and insects, hawking prey aerially or gleaning them from
vegetation. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Plants
- fruit
- Ficus (wild figs)
- Uapaca kirkiana (Mahobohobo)
- Syzygium guineense (Pale-bark waterberry)
- Grewia retinervis (Kalahari raisin)
- Pappea capensis (Jacket-plum)
- Morus (mulberries)
- Psidium (guavas)
- Persea (avocados)
- nectar
- Erythrina latissima (Broad-leaved coral tree)
- Insects
Breeding
- Monogamous, facultative cooperative breeder, as the breeding pair are
assisted by 1-6 helpers.
- The nest is an excavated hole in a dead branch, which often has several holes
from different breeding seasons; it may also use the old
nest of a Black-collared barbet.
- Egg-laying season is from September-January, peaking from
September-October.
- It lays 3-6 eggs eggs on a bed of wood chips.
- The chicks are fed by both parents and group members, leaving the nest
after about 49 days.
Threats
Status uncertain, although it is vulnerable to the clearing
of indigenous woodland for agriculture.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
