|
Laniarius ferrugineus (Southern
boubou)
Suidelike waterfiskaal [Afrikaans]; Igqubusha [Xhosa];
iBhoboni (also applied to Black-backed puffback), iGqumusha [Zulu]; Hwilo,
Samjukwa, Xighigwa [Tsonga]; Waterfiskaal [Dutch]; Gonolek boubou [French];
Flötenwürger [German]; Picanço-ferrugíneo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Malaconotidae
 |
|
Southern boubou, Kirstenbosch Botanical Gardens,
South Africa. [photo Trevor Hardaker ©] |
 |
 |
|
Southern boubou. [photo
Johann du Preez
©] |
Southern boubou at nest with chick. [photo Peter
Steyn ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to southern Africa, occurring from south-eastern
Botswana through Limpopo and North-West Provinces to southern Mozambique,
extending down the coast to KwaZulu-Natal, Eastern and Western Capes. It
occupies a wide variety of woodland habitats, as well as coastal thickets, riverine scrub, alien tree plantations and suburban gardens.
|
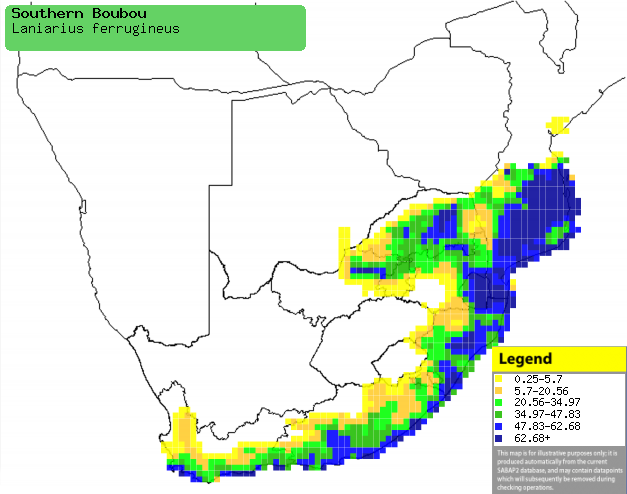 |
|
Distribution of Southern boubou in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Jacobin cuckoo.
Food
Highly adaptable, it eats a variety of animals and
occasionaly plants, most of which are caught on the ground. It also gleans
insects off leaves and bark and occasionally hawks flying insects. The following
food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Animals
- Invertebrates
-
Hymenoptera
- bees
- ants
- wasps
- Braconidae
- Tiphiidae
- Ichneumonidae
-
Lepidoptera
- caterpillars
- eggs and larvae
-
Coleoptera (beetles)
- dung beetles (Scarabaeidae)
- toktokkie beetles (Tenebrionidae)
- weevils (Curculionidae)
- plant-eating beetles
-
Orthoptera (crickets and grasshoppers)
- Acanthacris ruficornis (Garden locust)
- other grasshoppers
- earthworms
- ticks
- snails
- Helix adspersa
- Theba pisana
- Vertebrates
- Phyllodactylus porphyreus (Marbled leaf-toed gecko)
- Other birds
- Rodents
- Plants
- Fruit
- Lycium campanulatum (honey-thorn)
- Scutia myrtina (Cat-thorn)
- Seeds
- Datura ferox (Stinkblaar)
- loose grain
- Nectar
- Aloe arborescens (Krantz aloe)
- Aloe ferox (Bitter aloe
- Young plant shoots
- Miscellaneous
- breadcrumbs
- discarded porridge
Breeding
- The nest is built solely by the female and is an untidy, loosely woven
bowl made of twigs, roots and grasses, sometimes bound with spider web. It
is usually placed in a fork of a tree or bush, concealed by foliage. If the
nest is repeatedly disturbed, the breeding pair rip it apart and, using the
same materials, rebuild it nearby.
- Egg-laying season is from about August-March, peaking around
September-December.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for about 16-17
days.
- The chicks leave the nest at about 16-17 days old, becoming
semi-independent after about 8 weeks, after which they remain with their
parents for roughly 3 weeks more.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
