Telophorus zeylonus (Bokmakierie)
Bokmakierie [Afrikaans]; Ingqwangi [Xhosa]; iNkovu
[Zulu]; Ptjemptjete, Pjempjete [South Sotho]; Pšempšetle [North Sotho];
bokmakierie-klauwier [Dutch]; Gladiateur bacbakiri [French]; Bokmakiri [German];
Boquemaquire [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Malaconotidae
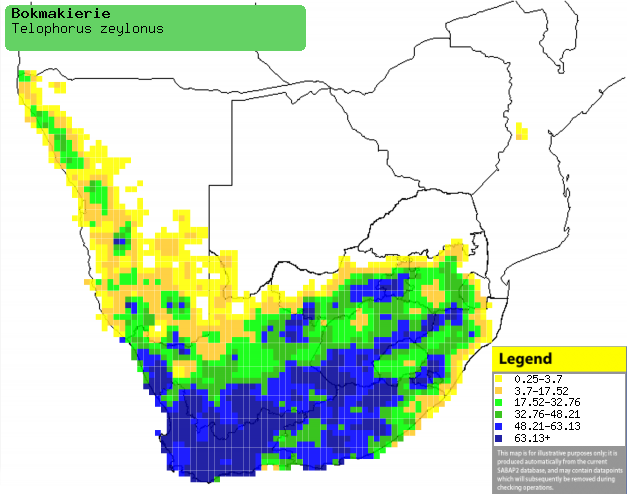
Distribution and habitat
Near endemic to southern Africa, it occurs across South
Africa excluding much of the Limpopo Province, extending into southern and
western Namibia and south-western Angola. It also has an isolated population
around the Chimanimani Mountain along the Zimbabwe/Mozambique border. It
occupies a variety of habitats, however it prefers open areas with scattered
shrubs and trees, such as dune scrub, succulent Karoo, renosterveld, Protea
scrub, open bushveld, alien tree plantations, bushclump grassveld, orchards,
vineyards, gardens, parks and bushy, rock-strewn hillsides.
|
 |
|
Distribution of Bokmakierie in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Jacobin cuckoo.
Food
An opportunistic feeder, it mainly eats insects but may
also feed on lizards, snakes, birds and fruit. It catches most of its prey on
the ground, rapidly pursuing before stunning and eating them. It also gleans
insects from leaves and branches and occasionally hawks prey aerially. The
following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Vertebrates
- Reptiles
- Amphibians
- Birds
- Plants
- Scutia myrtina (Cat thorn)
- Lycium ferocissimum (Snake-berry)
Breeding
- Both sexes construct the nest (see images below), which is a cup made of
small twigs, leaves, roots, tendrils, grass and bark, sometimes
incorporating man-made materials such as twine, paper and cardboard. It is
usually placed in a dense shrub, concealed by thick vegetation.
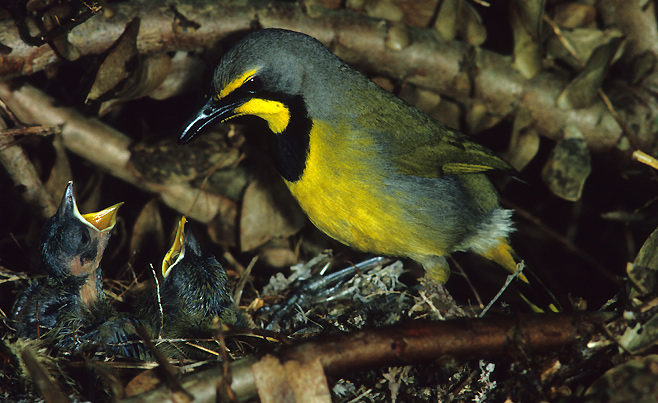 |
|
Bokmakierie at nest with hungry
chicks. [photo Peter Steyn ©] |
 |
|
|
Bokmakierie chicks in nest, South Africa. [photo
Johan van
Rensburg ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking during August.
- It lays 2-5 eggs, which are mainly incubated by the male in the day and
the female at night, for a period of about 14-19 days.
- The young are brooded and fed by both adults, leaving the nest after
about 15-21 days. The parents still tolerate their presence into the next
breeding season, at which point they become independent.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact widespread across sub-Saharan
Africa. s
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town
|
