|
Cercotrichas leucophrys (White-browed
scrub-robin)
[= Erythropygia leucophrys]
Gestreepte
wipstert [Afrikaans]; Eherekete [Kwangali]; Mtsherhitani [Tsonga];
Witbrauw-waaierstaart [Dutch]; Agrobate à dos roux [French];
Weißbrauen-heckensänger [German]; Rouxinol-do-mato-estriado [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Muscicapidae > Genus: Cercotrichas
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from Gabon to Somalia south through Tanzania,
southern DRC and Angola to southern Africa. Here it is common across the the
eastern half of South Africa through to Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana and
northern Namibia. It generally prefers valley bushveld and savanna woodland,
especially Acacia but also broad-leaved woodland, such as miombo (Brachystegia),
Mopane (Colosphermum mopane) and mixed terminalia (Terminalia) and
bushwillow (Combretum) woodland.
|
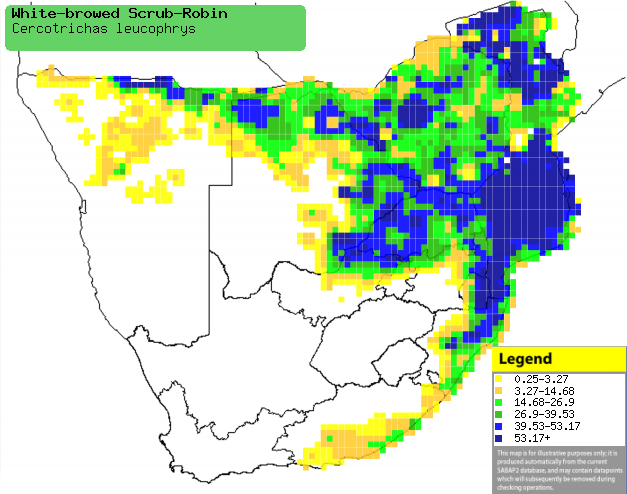 |
|
Distribution of White-browed scrub-robin in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Diderick
cuckoo and
Red-chested cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats invertebrates, doing most of its foraging on
the ground, flicking through leaves in search of prey and digging for foraging
termites. The following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Fruit
- Grewia flava (Velvet raisin)
- Vitex (fingerleafs)
- Nectar of Aloe marlothii (Mountain aloe)
Breeding
- Monogamous, territorial solitary nester, viciously defending its territory
against other White-browed scrub-robins, sometimes grappling with each other
in mid air before falling to the ground.
- The nest (see image below) is built solely by the female in about 4-5
days, consisting of a deep, untidy open cup built mainly of dry grass,
sometimes with a few twigs, dead Acacia leaves incorporated into the
structure. A lining of grass roots, flowerheads and leaves is also sometimes
added. It is typically placed in the center of a grass tuft at the base of a
tree, on the dead leaves of an aloe or in climbing grass tussocks on fallen
branches.
 |
|
|
White-browed scrub-robin nest with eggs,
Sericea farm, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from September-January, peaking from
September-November.
- It lays 2-4 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female.
- The chicks are frequently brooded by the female during the first few
days of their lives and are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after
about 11-12 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts - Birds of
southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker Bird Book
Fund, Cape Town.
|
