|
Lophotis ruficrista (Red-crested
korhaan)
[= Eupodotis ruficrista]
Boskorhaan [Afrikaans]; Epampa (generic term for korhaan)
[Kwangali]; Gaundya [Shona]; Xicololwana lexi tsongo [Tsonga]; Mokgwęba
[Tswana]; Zuidafrikaanse kuiftrap [Dutch]; Outarde houppette [French];
Rotschopftrappe [German]; Abetarda-de-poupa [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Gruiformes
> Family: Otitidae
The Red-crested korhaan is near-endemic to southern Africa,
being uncommon to locally common in a range of woodland habitats. It is
omnivorous, feeding on invertebrates, especially termites, beetles and
grasshoppers, and plant matter, especially seeds and fruit, foraging on the
ground, picking up food items with its bill. The male puts on a spectacular
courtship display to multiple females, who solely incubate the eggs and raise
the chicks. It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female, for
about 22 days, and little is known about the chicks.
Distribution and habitat
Near-endemic to southern Africa, occurring from southern
Angola and Zambia to Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, southern
Mozambique, Northern Cape and north-eastern South Africa. It is the most
woodland-dependent of the bustards and korhaans, occurring in Mopane (Colospermum
mopane), Acacia, cluster-leaf (Terminalia), Zambezi teak (Baikiaea
plurijaga) and miombo (Brachystegia) woodland.
|
 |
|
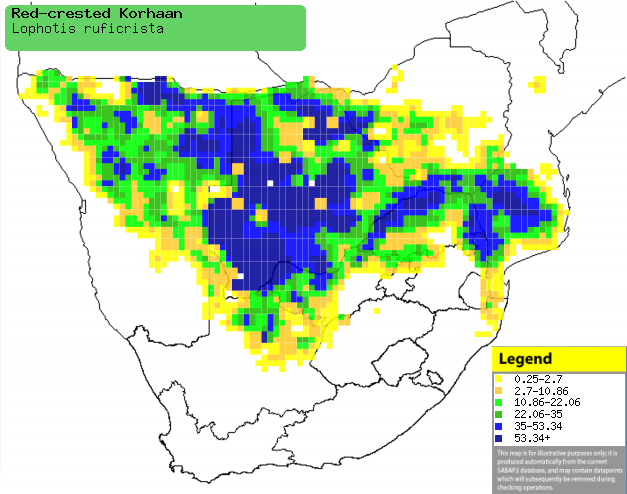
Distribution of Red-crested korhaan in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
Food
Eats mainly
invertebrates, supplemented with seeds and fruit. It mainly forages on the ground, picking up food items with
its bill. The following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- Invertebrates
- Plants
- seeds
- Acacia
- Brachystegia (miombo)
- Boscia albitrunca (Shepherds-tree)
- Citrulus (Tsamma lemon)
- Grewia flava (Brandybush)
- Grewia occidentalis (Cross-berry)
- Limeum (African flax)
- Lycium (honey-thorn)
- Rhus leptodictya (Mountain karee)
- leaves, and other soft plant material
- Blepharis integrifolia (klapperbossies)
- Monechma (skaapbloubossies)
- Genera of Acanthacaea
Breeding
- Polygynous, with each male
performing an elaborate courtship display to multiple females, some of which
he will mate with.
- It lays its eggs directly on the ground, often among dense leaf-litter.
 |
|
|
Red-crested korhaan at its nest, Nylsvley area,
South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- Egg-laying season is from September-April, peaking from
October-February.
- It lays 1-2 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about 22
days.
- Little is known about the young, except that they fledge at roughly six
weeks old.
Threats
No threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
