Phalacrocorax africanus (Reed
cormorant)
Rietduiker [Afrikaans]; Ugwidi (generic
term for cormorants) [Xhosa]; iPhishamanzi, uLondo [Zulu]; Nkororo (generic term
for cormorant) [Kwangali]; Timeletsane-ntšo [South Sotho]; Afrikaanse
dwergaalscholver [Dutch]; Cormoran africain [French]; Riedscharbe [German];
Corvo-marinho-africano [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Ciconiiformes
>
Family: Phalacrocoracidae
 |
|
Reed cormorant, Strandfontein Sewage Works, South Africa. [photo
Duncan Robertson
©] |
 |
 |
| Reed cormorant, Plettenberg Bay,
Western Cape, South Africa. [photo
Duncan Robertson
©] |
Reed Cormorant, Rondevlei Nature Reserve, Western
Cape, South Africa. [photo Duncan Robertson
©] |
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across much of sub-Saharan Africa; in southern
Africa, it is common in Zimbabwe, northern and
eastern Botswana, patches of Namibia, Mozambique and much of South Africa,
largely excluding the arid Kalahari. It can occupy almost any freshwater habitat,
excluding very fast-flowing streams, but it generally prefers bodies of water
with gently sloping shores.
|
 |
|
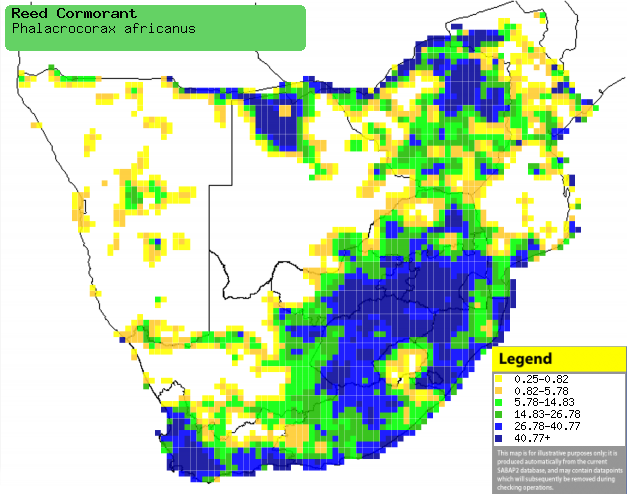
Distribution of Reed cormorant in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Predators and parasites
Movements and migrations
Resident and partially migratory, generally
moving to coastal areas in winter and inland waters in summer.
Food
It mainly eats fish and frogs, hunting by pursuing them through
the water using its large webbed feet. Its mainly forages in water under two
metres in depth, staying underwater for up to about 43 seconds. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
- Vertebrates
- fish
- Orechromis mossambicus (Mozambique tilapia)
- Solea bleekeri (Blackhand sole)
- Acanthopagrus berda (Riverbream)
- Barbus anoplus (Chubbyhead barb)
- Micropterus salmoides (Largemouth bass)
- Xenopus laevis (Common platanna)
- Rana angolensis (Common river frog)
- Cacosternu boetgeri (Common caco)
- Cyprinus carpio (Carp)
- Labeo umbratus (Moggel)
- frogs
- Xenopus laevis (Common platanna)
- Rana angolensis (Common river frog)
- Cacosternum boetgeri (Common caco)
- small birds
- Invertebrates
- insects
- molluscs
- Potomonautes warreni (Warren's crab)
Breeding
- Monogamous and usually colonial, joining other waterbirds such as
Cattle egrets,
African darters and
Grey and
Black-headed herons in
colonies of 10-50 breeding pairs. The male selects the nest site and
promptly displays to passing females by thrusting its head back and forwards
while flapping its wings.
- The nest (see image below) is built by both sexes in about a week,
consisting of a messy platform of sticks and dead reeds, with a cup in the
centre which is lined with grass. It is typically placed in the fork of a
tree over water, or in a large reedbed or even on the ground.
- Egg-laying season is year-round, peaking from August-October in the
Western Cape and from October-January elsewhere.
- It lays 1-6, usually 3-4 eggs, which are incubated by both sexes for
about 23-24 days.
- The chicks are fed by both parents, leaving the nest after
about three weeks. They become fully independent about four weeks after
fledging.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact it has greatly benefited from dam
construction.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
