|
Ploceus rubiginosus
(Chestnut weaver)
Bruinwewer [Afrikaans]; Kastanjewever [Dutch]; Tisserin
roux [French]; Rotbrauner weber, Maronenweber [German]; Tecel„o-canela
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Ploceidae
> Genus: Ploceus
Distribution and habitat
Occurs in two separate areas of sub-Saharan Africa; one
extending from Ethiopia to Tanzania and the other population restricted to
south-western Angola and southern Africa. Here it is locally common in northern
and central Namibia and north-western Botswana, generally preferring dry
thornveld and riverine woodland.
|
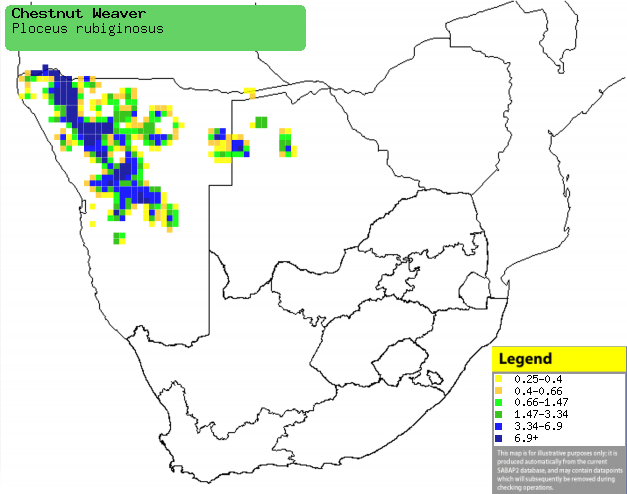 |
|
Distribution of Chestnut weaver in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Predators and parasites
The eggs and chicks have been recorded as food of Cape
crows (Corvus
capensis).
Food
It mainly eats the seeds of grasses, especially Guinea
grasses (Panicum), supplemented with nectar of Aloe species.
Breeding
- Polygynous and highly colonial, usually breeding in huge colonies of at
least 200 nests in a single tree, but sometimes in over 100 adjacent trees
each with 40-100 nests!
- The nest is built solely by the male, consisting of a retort-shaped
structure with a short entrance tunnel at the base. It is usually woven from
grasses such as Common nine-awned grass (Enneapogonn cenchroides),
love grasses (Eragrostis) and bushman grass (Stipagrostis),
and if accepted by the female she lines it with grass seed heads. It is
typically strung from the tip of a branch of a tree, such as Acacia,
Albizia and Mopane (Colosphermum mopane), about 3-8 metres
above ground.
- It breeds in response to rainfall with an egg-laying season from
December-May, peaking from January-March.
- It lays 1-6 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
11-14 days.
- The chicks are fed by the female only on a diet of mainly insects, such
as
caterpillars, grasshoppers and crickets (Orthoptera),
leaving the nest after about 13-16 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
