|
Turdoides gymnogenys
(Bare-cheeked babbler)
Kaalwangkatlagter [Afrikaans]; Siwerewere (generic term for
babbler) [Kwangali]; Naaktwangbabbelaar [Dutch]; Cratérope à joues nues
[French]; Nacktohrdroßling [German]; Zaragateiro-de-faces-nuas
[Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sylviidae > Genus: Turdoides
 |
 |
| Bare-cheeked babblers, Kunene River
Lodge, Namibia. [photo Trevor
Hardaker ©] |
Distribution and habitat
Near endemic to northern Namibia, as its distribution
marginally extends into south-western Angola. It generally prefers undergrowth
along dry rivers and streams, as well as open woodland with thickets on
boulder-strewn hillsides and plains.
|
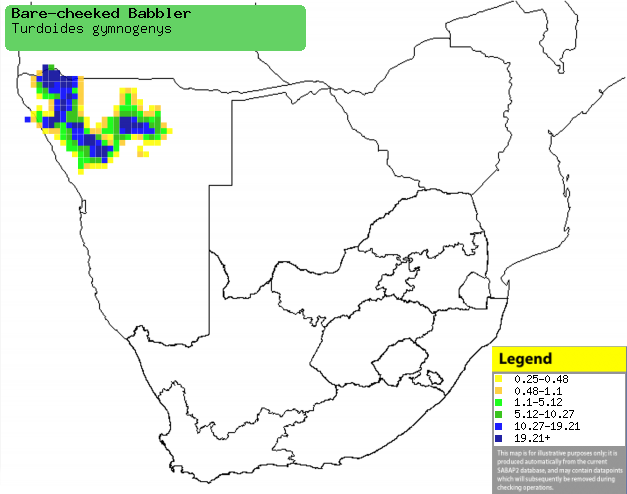 |
|
Distribution of Bare-cheeked babbler in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Levaillant's cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats arthropods such as beetles (Coleoptera),
mantids and
caterpillars, foraging in groups on the ground in the undergrowth. The
groups loud calling while foraging often attracts other bird species, so the
group becomes the center of a mixed species foraging flock.
Breeding
- Cooperative breeder, living in noisy groups of 2-11, usually 4-6 birds.
- The nest is a large, loosely built bowl made of herb stems and dry
grass, lined with finer plant material. It is typically placed in a multiple
fork in the center of a Terminalia or Tamboti (Spirostachys
africana) tree. ]
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which hatch into chicks that are cared for by all
group members.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
