|
Turdoides hartlaubii
(Hartlaub's babbler)
Witkruiskatlagter [Afrikaans]; Siwerewere (generic term for
babbler) [Kwangali]; Letshêganôga [Tswana]; Hartlaub-babbelaar [Dutch];
Cratérope de Hartlaub [French]; Weißbürzeldroßling [German];
Zaragateiro-de-rabadilha-branca [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) >
Order: Passeriformes > Family: Sylviidae
> Genus: Turdoides
Distribution and habitat
Occurs from south-eastern DRC through Zambia and Angola to
southern Africa. Here it is locally common in dense, tall woodland along
watercourses, reedbeds and Papyrus (Cyperus papyrus) swamps in northern
Botswana and northern Namibia (including the Caprivi Strip).
|
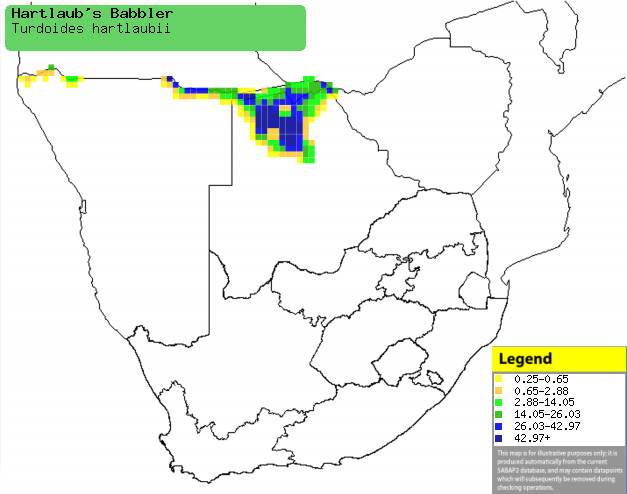 |
|
Distribution of Hartlaub's babbler in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common). |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Levaillant's cuckoo.
Food
Its diet is unknown, however it has been observed foraging
on the ground in dense vegetation, often along with
Arrow-marked babblers.
Breeding
- It is a cooperative breeder, living in year-round groups of 5-20, usually
8 birds.
- The nest is a rather messy bowl built of dry leaves, grass, string and
thin roots, lined with finer plant material such as slender twigs. It
typically places the nest close to water, such as in a clump of reeds, flood
debris attached to a tree or bush, or in a small tree in a swamp or
flood plain.
- Egg-laying season is from October-April.
- It lays 2-4 glossy, greyish turquoise or deep greenish blue eggs.
- The chicks are cared for by both parents and helpers, leaving the nest
after about 18 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
