|
Prionace glauca (Blue shark)
(Linnaeus, 1758)
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) >.Chondrichthyes >
Elasmobranchii > Galeomorphii >
Carcharhiniformes >
Carcharhinidae
 |
|
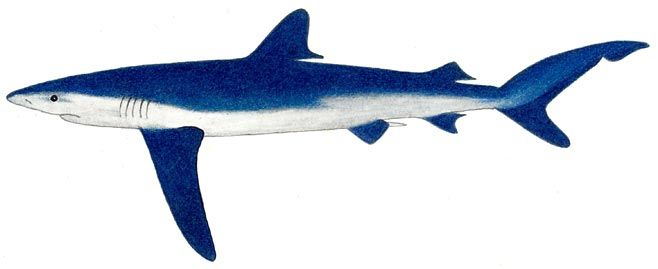
Prionace glauca (Blue shark) [Illustration
by Ann Hecht ©] |
Identification
A slim, graceful, blue shark with a long
conical snout, large eyes, curved, saw-edged, triangular upper
teeth, long narrow pectoral fins, 1st dorsal fin well behind
pectorals, and no interdorsal ridge. Upper surface dark blue, sides
bright blue, underside white.
Size
To 3.8 m and possibly longer.
Range
Offshore along the entire coast; circumglobal in temperate
and tropical seas.
Habitat
Oceanic but approaching inshore in areas
with narrow shelves, surface to over 152 m.
Biology
Common, often
seen at the surface. Bears up to 135 young. Eats bony fish,
including sardines and other herring-like fishes, anchovies, eels,
needlefish, sauries, flyingfish, hake and other cod-like fishes,
tuna, mackerel, and jacks, also small sharks, squid, pelagic red
crabs, cetacean carrion, occasional sea birds, and garbage. Usually
fairly timid when approached by divers.
Human Impact
Dangerous to
offshore divers and victims of maritime accidents. Occasionally
taken by anglers, but mostly caught by offshore longliners.
Text by Leonard J.V. Compagno, David A. Ebert
and Malcolm J. Smale
|
