|
Eurystomus glaucurus
(Broad-billed roller)
Geelbektroupant [Afrikaans]; Breedbekscharrelaar
roller [Dutch]; Rolle violet [French]; Zimtroller [German];
Rolieiro-de-bico-amarelo [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes
>
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa
(animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia >
Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial vertebrates) >
Tetrapoda (four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia
(reptiles) > Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria (dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory
dinosaurs) > Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves (birds)
> Order: Coraciiformes > Family:
Coraciidae
The Broad-billed roller is found from Senegal east to
Somalia, extending south to Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana and north-eastern
South Africa. Here it is fairly common in savanna, as well as clearings in
woodlands. It is a specialist predator, mainly eating swarming termite and ant
alates, as well as beetles and bugs. It mainly nests in unlined cavities in
trees 5-15 m above ground. It also nests in holes of barns (recorded in
Zimbabwe). It lays 2-4 eggs, timing laying to coincide with the emergence of
insects after rain.
Distribution and habitat
Occurs across sub-Saharan Africa; in southern Africa it is
fairly common in the Caprivi Strip (Namibia), northern and eastern Botswana,
Zimbabwe, Mozambique and north-eastern South Africa. It generally prefers savanna
and clearings in woodlands.
|
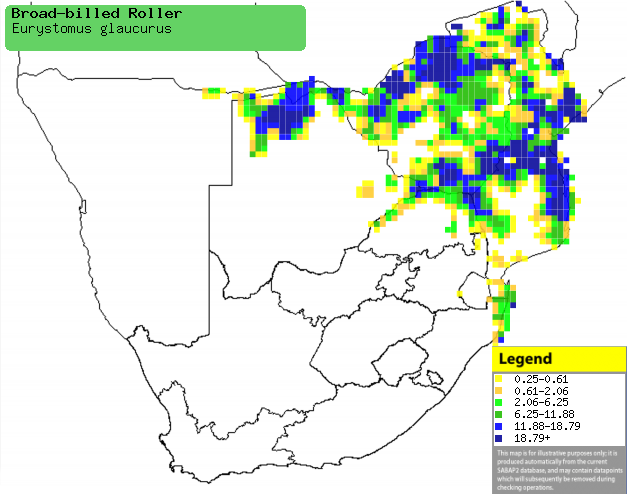 |
|
Distribution of Broad-billed roller in southern
Africa, based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird
Atlas Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Movements
Intra-African breeding migrant, mainly breeding in southern Africa
before moving north in the non-breeding season.
Flocks start to arrive in southern Africa in September, leaving in the period
from December to April.
Food
It is a specialist predator, mainly eating swarming termite
and ant alates, as well as beetles and bugs. It hunts aerially, often in large
flocks. The following percentages indicate the proportion of that food item in
its diet, (e.g. roughly 9% of its diet is beetles). In one study, the
following food items have been recorded in its diet:
- ant alates - 66%
-
termite alates - 15%
- Macrotermes
- Pseudocanthotermes
-
Coleoptera
(beetles)) - 9%
-
Hemiptera (bugs) - 7%
- Lygaeidae
- Pentatomidae
- Plataspidae
- Reduviidae
- Coreidae
- Jassidae
- Cicadidae
- Other insects - 3%
Breeding
- It mainly nests in unlined cavities about 5-15 m above ground, usually in
a tree but occasionally in a barn.
 |
|
|
Broad-billed roller in its tree hollow, Kruger
Park, South Africa. [photo Warwick Tarboton ©] |
|
- It lays 2-4 eggs, typically timed with the emergence of
insects after rain.
Threats
Not threatened, in fact common in many areas of southern
Africa.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG (eds) 2005. Roberts -
Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
