|
Cercotrichas quadrivirgata (Bearded
scrub-robin)
[= Erythropygia quadrivirgata]
Baardwipstert
[Afrikaans]; Streepkop-waaierstaart [Dutch]; Agrobate à moustaches
[French]; Brauner bartheckensänger [German]; Rouxinol-do-mato-de-bigodes
[Portuguese]
Life > Eukaryotes > Opisthokonta > Metazoa (animals) > Bilateria > Deuterostomia > Chordata > Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class: Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial vertebrates) > Tetrapoda (four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota > Reptilia (reptiles) > Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria > Dinosauria (dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) > Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves (birds) > Order: Passeriformes > Family: Muscicapidae > Genus: Cercotrichas
Distribution and habitat
It occurs from southern Somalia through eastern Tanzania to
Malawi, Zambia and southern Africa. Here it is locally common in Zimbabwe,
Mozambique, northern Botswana, Caprivi Strip (Namibia) and the extreme east of
South Africa. It generally prefers sand forest, thickets in broad-leaved
woodland or savanna and riverine forest.
|
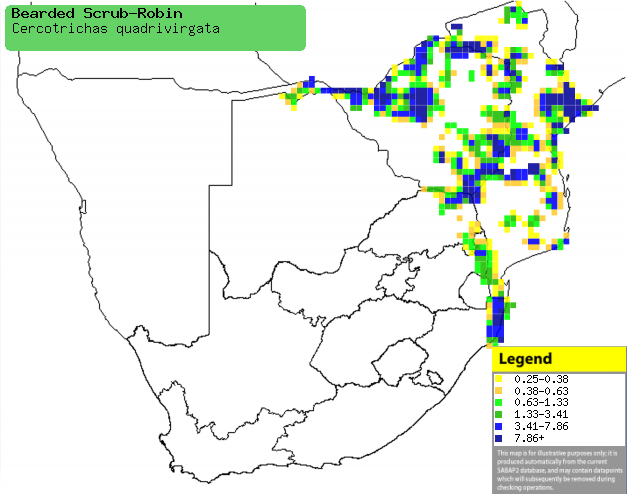 |
|
Distribution of Bearded scrub-robin in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Brood parasites
It has been recorded as host of the
Red-chested cuckoo.
Food
It mainly eats beetles and ants, doing most of its foraging
on the ground, often taking prey flushed by driver ant swarms. It may also
forage high up in the tree canopy, gleaning ants and caterpillars from leaves
and branches. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The nest is an open cup set into a pad of rootlets and dead leaves,
sometimes also including lichen, dried grass, small twigs and moss, lined
with animal hair such as that of the Nyala (Tragelaphus angasi),
Bushpig (Potomachoerus larvatus) and Red duiker (Cephalophus
natalensis). It is typically placed in a rotten cavity in a living tree,
on top of a hollow stump or in a hole at the base of a fork against the tree
trunk.
- Egg-laying season is from September-December.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
11-14 days.
- The chicks are fed by both adults, leaving the nest after about 15-17
days, after which they still remain dependent on their parents for about 4
more weeks.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
