|
Stenostira scita (Fairy
flycatcher)
FeevlieŽvanger [Afrikaans]; Elf-apalis [Dutch];
…rythrocerque de Livingstone [French]; Livingstones rotschwanzschnšpper
[German]; Papa-moscas-d'asa-branca [Portuguese]
Life
> Eukaryotes >
Opisthokonta
> Metazoa (animals) >
Bilateria >
Deuterostomia > Chordata >
Craniata > Vertebrata (vertebrates) > Gnathostomata (jawed
vertebrates) > Teleostomi (teleost fish) > Osteichthyes (bony fish) > Class:
Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned
fish) > Stegocephalia (terrestrial
vertebrates) > Tetrapoda
(four-legged vertebrates) > Reptiliomorpha > Amniota >
Reptilia (reptiles) >
Romeriida > Diapsida > Archosauromorpha > Archosauria >
Dinosauria
(dinosaurs) > Saurischia > Theropoda (bipedal predatory dinosaurs) >
Coelurosauria > Maniraptora > Aves
(birds) > Order: Passeriformes
> Family: Sylviidae
Distribution and habitat
Endemic to southern Africa, with the bulk of its population
scattered across South Africa, excluding the lowland coastal forests of the
Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal and extending marginally into southern Botswana
and Namibia. During the breeding season it favours shrublands, such as Karoo,
fynbos, thorny thickets, mountain scrub and sweet grassland. In winter it moves
into more wooded habitats, including Acacia savanna, plantations and
gardens.
|
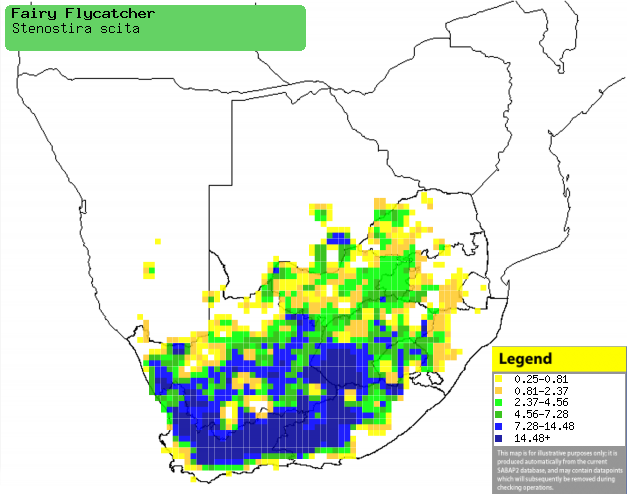 |
|
Distribution of Fairy flycatcher in southern Africa,
based on statistical smoothing of the records from first SA Bird Atlas
Project (©
Animal Demography unit, University of
Cape Town; smoothing by Birgit Erni and Francesca Little). Colours range
from dark blue (most common) through to yellow (least common).
See here for the latest distribution
from the SABAP2. |
Food
It solely eats insects, often making short sallies from a
perch to hawk prey aerially. It also joins mixed species foraging flocks, and it
may glean insects from flowerheads. The following food items have been recorded
in its diet:
Breeding
- The female solely builds the nest, which is a small cup with thick, compact sides, consisting of grass, dead leaves, bark shreds and bound with spider webs; it has a thick lining of wool, hair, feathers and plant down. The nest is camouflaged well in shrubby vegetation, sometimes placed as low as 20 cm above the ground.
 |
|
Fairy flycatcher sitting on its nest. [photo Peter
Steyn ©] |
- Breeding season is mainly October to December.
- It lays 2-3 eggs, which are incubated solely by the female for about
17-18 days.
Threats
Not threatened.
References
-
Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ and Ryan PG 2005. Roberts
- Birds of southern Africa, VIIth ed. The Trustees of the John Voelcker
Bird Book Fund, Cape Town.
|
